The SPI communicates via 4 ports which are:
- MOSI – Master Data Output, Slave Data Input
- MISO – master data input, slave data output
- SCLK – clock signal, generated by the master device, up to fPCLK/2, slave mode frequency up to fCPU/2
- NSS – Slave enabled signal, controlled by the master device, some ICs will be labelled as CS (Chip select)
Advantages of using SPI
- The protocol is simple as there is no complicated slave addressing system like I2C.
- It is the fastest protocol compared to UART and I2C.
- No start and stop bits unlike UART which means data can be transmitted continuously without interruption
- Separate MISO and MOSI lines which means data can be transmitted and received at the same time
Disadvantages of using SPI
- More Pin ports are occupied, the practical limit to a number of devices.
- There is no flow control specified, and no acknowledgement mechanism confirms whether data is received unlike I2C
- Uses four lines – MOSI, MISO, NCLK, NSS
- No form of error check unlike in UART (using parity bit)
- Only 1 master
Of course, the blog on the communication protocol of SPI cannot be missed, because there are blogs dedicated to I2C and UART. You can learn about this blog through SPI – Introduction to Serial Peripheral Interface
Examples of SPI in Microcontrollers:
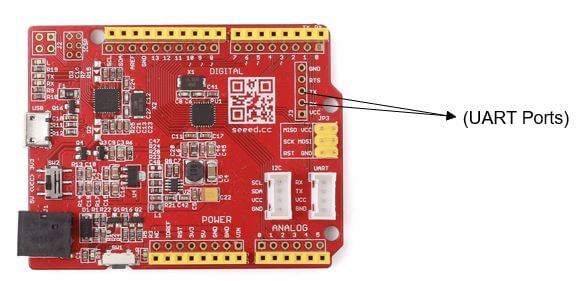
SPI Seeeduino V4.2
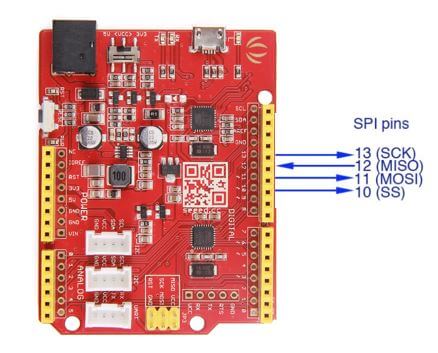
- SPI serial communication can be used with Arduino for communication between two Arduinos where one Arduino will act as master and another one will act as a slave.
- Used to communicate over short distances at high speed.
- This is the same product: Arduino v4.2 from the above UART example
MCP 3008 / Grove I2C ADC
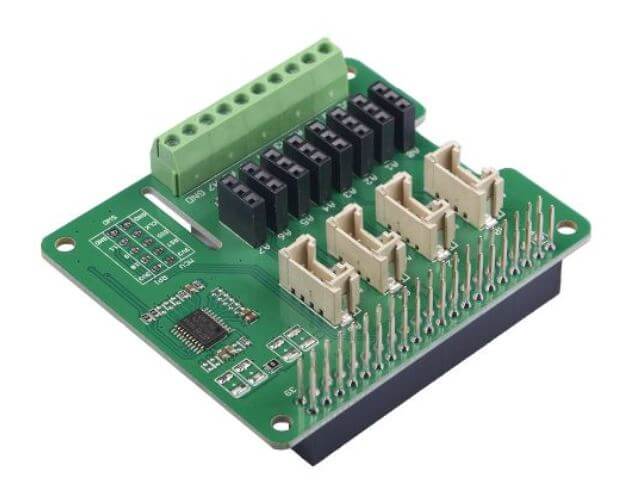
- Seeed does offer a similar product which has the same functions: Grove I2C ADC but its communication peripheral is I2C.
- It is 10 bit 8-channel analogue-to-digital converter (ADC).
- For the MCP 3008, it connects to the Raspberry Pi using an SPI serial connection. Done by using the hardware SPI bus or any four GPIO pins and software SPI to connect to the MCP 3008.
Serial CAN-BUS Module based on MCP2551 and MCP2515

- This Seeed product: Serial CAN Bus module provides your Arduino with CAN bus capabilities and allows you to hack your vehicle. It lets you read and write messages to the CAN bus.
- CAN bus is a messaging protocol system that lets various microcontrollers and sensors within a vehicle to talk to each other. CAN provides long-distance, medium communication speed, and high reliability.
- This Serial CAN Bus module can also be connected to your Arduino through the on-board Grove connector.
- Interfaces with microcontrollers via SPI.
ENC28J60 OVERLAYS HAT for Raspberry pi

- The Pi zero ENC28J60 is a simple Network Adapter module for Pi zero that is very easy to assemble and configure.
- It allows your Raspberry Pi zero to access the network smoothly, and it is easy to do system updates and software installation operations.
- Microchip’s ENC28J60 is a 28-pin, 10BASE-T stand-alone Ethernet controller with an SPI interface.
- The SPI interface serves as a communication channel between the host controller and the ENC28J60.
SPI Driver/Adapter-Easily Driver SPI Devices
- This is a similar product as the I2C Driver/Adapter-Easily Driver I2C Device but for SPI instead. It is an easy-to-use tool for controlling SPI devices. It works with Windows, Mac, and Linux, and has a built-in colour screen that shows a live logic-analyzer display of all SPI traffic.
- Similarly, it uses a standard FTDI USB serial chip to talk to the PC, so no special drivers need to be installed. The board includes 3.3 and 5 V supplies with voltage and current monitoring.
- SPI flash is very common, and by using a test clip, SPIDriver makes it convenient to read and write SPI flash in-circuit. A short script is all it takes to read or write an Atmel’s flash and SPI LED strips are also easy to hook up to the SPI Driver, You can also be able to control them directly which makes them much more fun!
- Using SPI in this secnario is fast enough to smoothly animate long strips and achieve POV effects. Short strips can also be powered directly by the SPIDriver’s beefy 470 mA built-in supply.
So, which of these communication peripherals is the “best”? UART, SPI or I2C?
Unfortunately, there is no “best” communication peripheral. Each communication peripheral has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Thus, a user should pick a communication peripheral that suits your project the best. For example, you want the fastest communication peripheral, SPI would be the ideal pick. On another hand, if a user wants to connect many devices without it being too complex, I2C will be the ideal pick as it can connect up to 127 devices and it is simple to manage.
Summary
In summary, I have compiled all the various advantages/disadvantages and functions of the various communication protocols and compared them so you can easily pick which is the best for your project. Do keep in mind that the device, accessory, module or sensor you are using must support the communication protocol as well.
| Protocol | UART | I2C | SPI |
|---|
| Complexity | Simple | Easy to chain multiple devices | Complex as device
increases |
| Speed | Slowest | Faster than UART | Fastest |
| Number of devices | Up to 2 devices | Up to 127, but gets complex | Many, but gets complex |
| Number of wires | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| Duplex | Full Duplex | Half Duplex | Full Duplex |
| No. of masters and slaves | Single to Single | Multiple slaves and masters | 1 master, multiple slaves |
Exclusive offer!
Seeed is offering one free breadboard for each customer, apply the code BREADBOARD to get one free breadboard (U.P. $4.90) at Seeed!